LAU Sustainability Strategy

Lebanese American University
Sustainability Strategy
2025-2030
Introduction
The Lebanese American University (LAU) aims to make a meaningful and positive impact through comprehensive and inclusive sustainability practices. The Office for Sustainability (OfS) is actively striving to develop an extensive, data-driven, university-wide Sustainability Strategy that is connected to the University’s mission and core values while providing a clear pathway for action. This strategy is built on four pillars, emphasizing a data-driven approach to identifying and addressing the University’s most significant impacts and contributions to communities nationally, regionally, and globally.
Approach
In order to develop this strategy, the OfS created and followed a roadmap consisting of five main phases (see Figure 1):
In the first phase, a desk work and research was conducted by the OfS to craft the Strategy vision and mission statements and identify pillars that will guide sustainability actions within LAU.
Phase two involved launching a survey among faculty members, staff, and students to explore perspectives on sustainability, with a focus on awareness, teaching, research, and engagement. The survey gathered data, offering a comprehensive view of current practices and attitudes.
In phase three, faculty, staff, and students participated in dedicated Strategy Workshops on both LAU campuses, Beirut and Byblos, to provide valuable insights from across the institution. Efforts were made to ensure inclusivity and capture the diverse perspectives of the LAU community. Participants conducted a SWOT analysis for each of the four pillars established in phase one, identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats both within and beyond LAU. They then formulated a set of activities aligned with each pillar.
Phases four consisted of two main activities. First, based on the collected feedback from the surveys and the Strategy Workshops, the OfS categorized the proposed activities into themes for each pillar. Then, with the support of the university president and upper administration members (VPs, Deans, Directors, etc.), a Sustainability Task Force (STF) was established representing various University offices, departments and schools. The STF was charged with prioritizing the proposed activities, assigning ownership, allocating budgets, and defining monitoring processes.
In the final phase, Phase Five, the OfS and the STF refined the strategy’s focus areas to ensure alignment with LAU’s priorities. Additionally, action plans for prioritized activities were developed for implementation over the next five years, in line with the Agenda 2030 timeline.
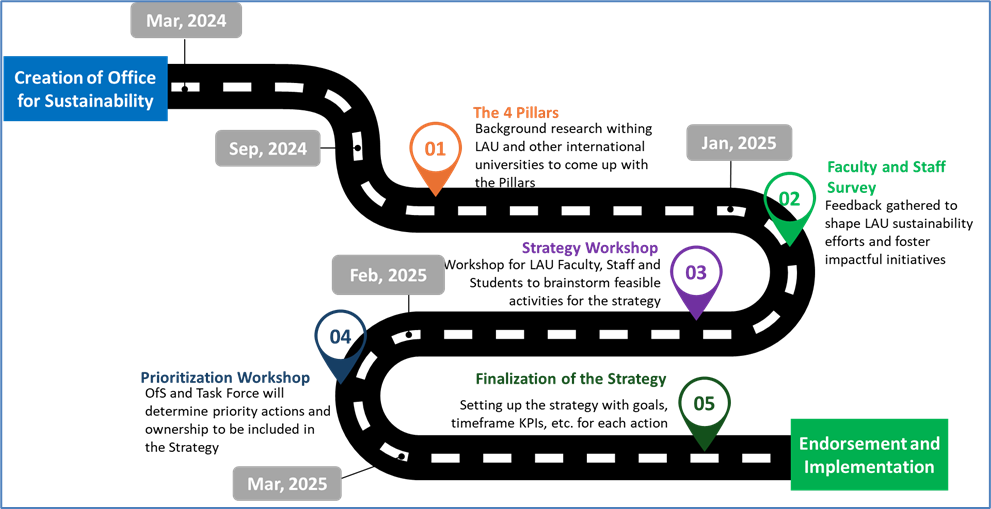
Figure 1: LAU Sustainability Strategy Roadmap
LAU Sustainability Strategy
This strategy brings together various university stakeholders, governance structures, and operational processes to establish a comprehensive and dynamic approach to sustainability. It is built on interconnected pillars, key actors, and strategic processes, ensuring effective implementation, monitoring, and continuous improvement.
The strategy is guided by the articulated strategy-specific vision and the OfS mission statement. Its implementation will be carried out through a tailored governance and leadership framework that aligns with the university’s structure.
Sustainability Strategy Vision
To cultivate a university culture where sustainability is embedded in education, research, community engagement, and operations—empowering students, faculty, and staff to lead in environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and sustainable resource use for a thriving future.
OfS Mission Statement
To foster a culture of sustainability across all university activities, including research, teaching, patient care, and facilities management with the goal of ensuring the university’s lasting positive environmental and social impact.
Governance and Leadership Structure
To implement the strategy, commitment and active engagement from essential enablers is needed at multiple governance levels. These enablers are:
- Upper Administration: Including the Board of Trustees, President’s Cabinet, Provost’s Office, Council of the Deans, and Committees. They set strategic direction, provide oversight, and high-level decision-making.
- Office for Sustainability (OfS): the OfS-dedicated personnel along with the STF are responsible for developing and overseeing the implementation of the strategy and initiatives across the university. They are also responsible for ensuring compliance, and integrating sustainability into university functions.
- Deans: Deans, department heads, and curriculum committees design and implement sustainability-focused courses, programs, and research projects.
- Research Centers and Hubs: Facilitate academic and research activities that align with sustainability goals and they also provide expertise and collaboration opportunities for integrating sustainability into curricula.
- Facilities Management: Oversees sustainable infrastructure, energy use, water conservation and reuse, solid and hazardous waste management, and other operational aspects of the university including the two hospitals.
These governance structures facilitate interaction among enablers through feedback, review, and reporting mechanisms, ensuring continuous assessment and improvement in the implementation and evolution of the sustainability strategy.
The Four Pillars of Sustainability
The sustainability strategy is built on four core pillars, each addressing a key area of impact. After an extensive review of relevant literature and the sustainability strategies of similar universities both regionally and globally, the OfS identified four pillars aligned with LAU’s mission and historic achievements. The four pillars and descriptive statement of each are:
- Conscientious Education: Inspiring students to understand the significance of sustainability and its effects on their personal and professional lives, while providing opportunities to engage with sustainability through both formal and informal curricula.
- Research for Sustainability: Leading research on the environment, social justice, and development in alignment with the UN’s Agenda 2030 and sharing findings with LAU’s community and policy-makers.
- Community Engagement: Fostering a sustainability mindset among students, faculty, staff, alumni, and local communities by serving as a hub for diverse expertise and experiences to engage in and influence sustainability research, education and outreach and enhancing broader university activities related to sustainability.
- Sustainable Use of LAU Resources: Spearheading sustainability initiatives in collaboration with all LAU communities and integrating sustainable practices into the operations of all the University’s campuses and hospitals. This pillar works closely with Facilities Management to implement sustainable operations.
To implement the strategy, activities for each pillar are grouped under specific themes. The university is committed to addressing these themes over the next five years, through 2030. The pillars and themes associated with them are presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Pillars and Associated Themes
For each of these themes, OfS along with STF have determined its aim, targets and a list of proposed activities (see Annex I: Themes for the Pillars). Every activity, identified through the convened workshops and surveys, has corresponding action plans that will be developed simultaneously by the relevant LAU body and published and monitored by OfS.
Stakeholder Engagement
The strategy recognizes multiple actors who contribute to sustainability efforts:
- Student Organizations: Engage students in sustainability leadership and activities.
- Faculty Members: Incorporate sustainability into teaching, research, and outreach.
- Staff: Support sustainability efforts through administration and operations.
- Physicians: Likely involved in health-related sustainability initiatives within LAUMCs.
- Alumni Networks: Advocate for sustainability and support initiatives through mentorship, funding, and networking opportunities.
- Community Members: including Government agencies, NGOs, and industry partners who collaborate with the university on sustainability research, projects, and funding opportunities. They also participate in collaborative sustainability projects.
These stakeholders contribute directly to the implementation of the four pillars.
Strategy Framework
The sustainability strategy is supported by structured processes that ensure effective planning, implementation, monitoring, and continuous improvement. These processes create a systematic approach to embedding sustainability across the university and ensuring accountability at all levels, as presented in the framework shown in Figure 3.
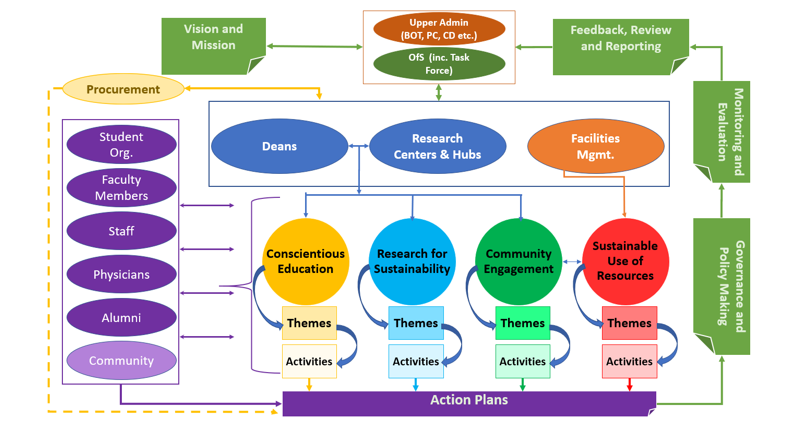
These processes include Procurement, Action Plans, Governance and Policy Making, Monitoring and Evaluation, and Feedback, Review, and Reporting.
Procurement
To ensure that the university’s purchasing decisions align with sustainability principles, prioritizing environmentally and socially responsible products and services:
- Develop and/or implement a Sustainable Procurement Policy that includes guidelines for selecting vendors based on environmental impact, fair labor practices, and ethical sourcing.
- Set procurement targets, such as purchasing locally sourced food, purchasing recycled material instead of first-use material, etc..
- Establish supplier evaluation criteria to ensure compliance with sustainability standards.
- Encourage green purchasing by prioritizing energy-efficient equipment, non-toxic materials, and biodegradable products.
Action Plans
To define concrete sustainability initiatives under each pillar, ensuring clear goals, responsibilities, and timelines:
- Develop a Sustainability Action Plan with short-term (1–3 years), medium-term (3–5 years), and long-term (5–10 years) goals.
- Assign responsibilities to key stakeholders, including the OfS, faculty members, student organizations, and administrative departments etc.
- Ensure regular updates to the action plan based on progress assessments and emerging sustainability challenges.
- Integrate the plan into relevant academic curricula, operational strategies, and campus-wide initiatives.
Governance and Policy Making
To establish clear policies, frameworks, and governance mechanisms that embed sustainability in the university’s decision-making process.
- Develop university-wide sustainability policies covering areas such as carbon neutrality, waste management, water conservation, sustainable construction, climate action, and ethical research.
- Establish a Sustainability Task Force comprising representatives from administration, faculty, student organizations, and facilities management to oversee policy implementation.
- Integrate sustainability principles into academic governance, ensuring that sustainability is embedded in curricula, research priorities, and faculty development programs.
- Align university policies with national and international sustainability standards, such as the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the like.
Monitoring and Evaluation
To track progress, measure impact, and ensure accountability in sustainability initiatives:
- Develop a Sustainability Performance Dashboard with Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for tracking progress on carbon footprint reduction, waste diversion rates, water and energy efficiency, and engagement levels.
- Conduct annual sustainability audits and reports to assess progress, identify gaps, and recommend improvements.
- Implement a data-driven decision-making approach by collecting and analyzing data on resource consumption, emissions, and behavioral change within the university community.
- Establish a feedback loop to allow faculty, students, and staff to contribute suggestions and report sustainability concerns.
Feedback, Review, and Reporting
To ensure transparency, stakeholder engagement, and continuous improvement of sustainability efforts:
- Publish annual sustainability reports summarizing achievements, challenges, and future plans, accessible to the university community and external partners.
- Conduct biannual stakeholder engagement sessions (town halls, surveys, and focus groups) to gather input and improve strategies.
- Establish a public feedback mechanism, where students and staff can suggest new initiatives or report issues through OfS website and other media channels.
- Benchmark performance against peer institutions and global sustainability rankings, such as the THE Impact Ranking, QS Sustainability Ranking and the like.
Conclusion
Implementing this strategy ensures that sustainability is embedded in every aspect of LAU’s operations, education, research, and community engagement. By adopting a structured and data-driven approach, the university can achieve measurable progress, foster a culture of sustainability, and contribute to global environmental and social goals. This document provides insights on strategic planning for sustainability at LAU through:
- Vision and Mission setting the overall direction, influencing governance, policies, and strategic initiatives.
- Upper Administration and the OfS overseeing implementation and coordinating with Deans, Research Centers, and Facilities Management.
- The four pillars defining key areas of action, supported by themes and activities within education, research, community engagement, and resource use.
- Stakeholders actively participating in these pillars, driving implementation at different levels.
- Processes such as procurement, governance, action plans, monitoring, and feedback ensuring sustainability initiatives are well-structured, continuously assessed, and improved.