SDG 13: Climate Action
SDG 13 focuses on climate action, urging global collaboration to combat climate change and its impacts. In alignment with this crucial objective, LAU has taken significant strides towards environmental sustainability and climate resilience. With a commitment to tracking and reducing carbon emissions, LAU is actively contributing to SDG 13 by implementing comprehensive strategies across its campuses and academic programs such as Minor in Climate Change and Sustainability Policy. From fostering research on environmental issues to raising consciousness about sustainable design, LAU is playing a pivotal role in promoting climate awareness and sustainable practices within its community and beyond. The university’s dedication to energy and water conservation, coupled with its continuous efforts to engage the community in green initiatives, demonstrates LAU’s commitment to addressing the urgent global challenge of climate change outlined in SDG 13.
Carbon Emissions
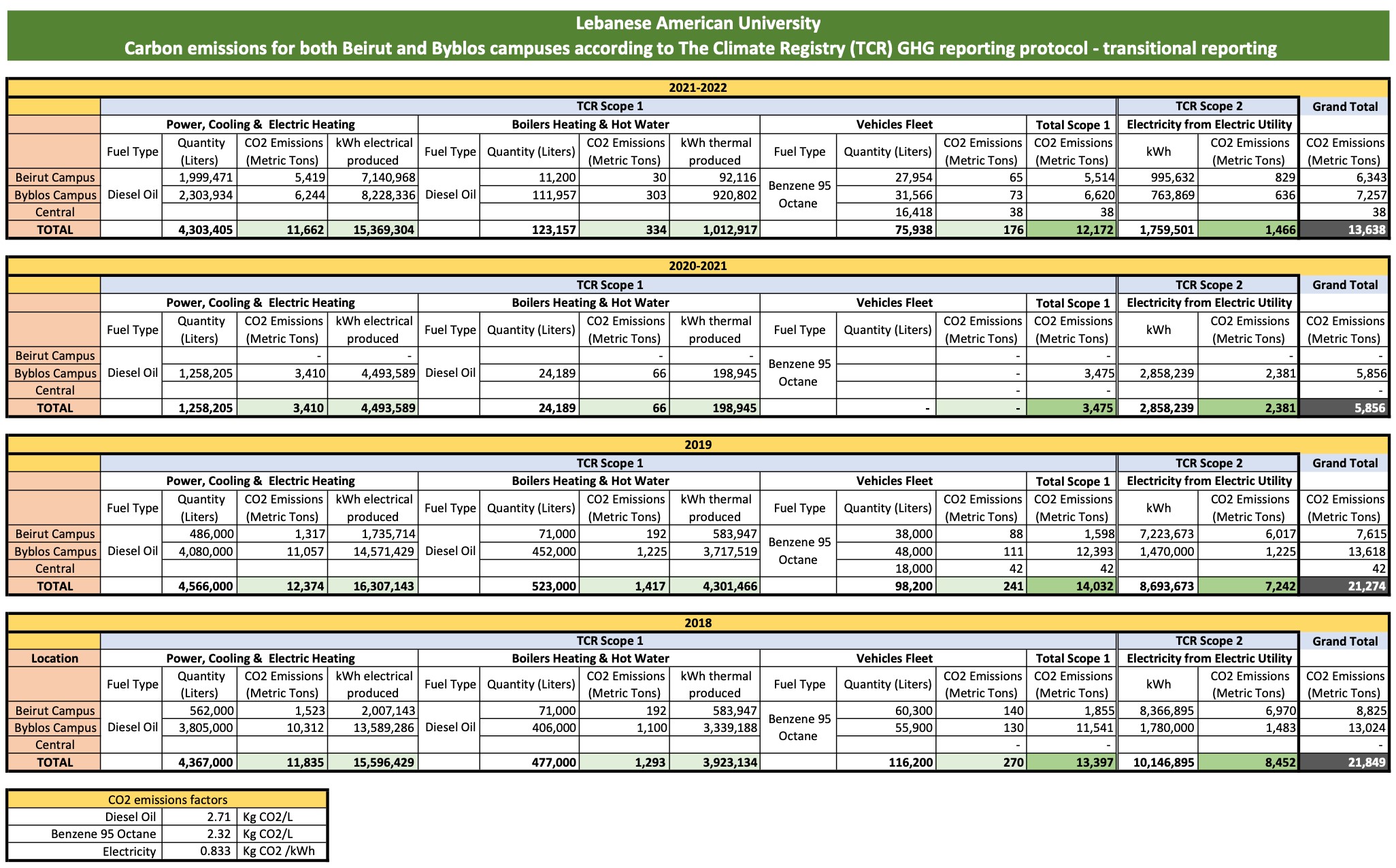
LAU is keen on tracking its carbon emissions in an effort to reduce them and ultimately become carbon neutral. The below table summarizes the Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions for Beirut and Byblos campuses as of 2018.
Institute for Environmental Studies and Research
The mission of the Institute of Environmental Studies & Research is to investigate issues of environmental nature, and the impact of such issues on the long-term sustainability of the region and its resources. These issues include but are not limited to: the impact of urban growth, zoning and urban development on cities and suburbs, and the impact of building construction and energy use on the environment. The objectives of the Institute would be to develop studies and proposals aimed at:
- Promoting sustainable practices, including land use strategies and demographic projections, specific to urban and suburban zones.
- Developing studies on urban planning, transportation systems, land management, and preservation of natural areas.
- Providing impact assessment for large scale projects such as industrial projects, infrastructure, and social housing.
- Conducting surveys of historical areas and proposing master plans for areas in need of development and/or preservation.
- Developing studies on improving energy conservation in buildings and innovative sustainable practices in building construction.
Anthony Brower: A Different Kind of Climate Change
The Institute for Environmental Studies & Research [IESR] hosted a lecture with Anthony Brower.
Anthony constantly redefines sustainable design by uncovering transformational patterns in the built environment that generate new design approaches that are responsive and responsible. An award winning architect, writer, public speaker and member of the USGBC college of Fellows whose passions around high performance building design and its potential impact on the built environment drive him to continually research and uncover how design needs to evolve to respond to the overwhelming and often paralyzing impacts of a rapidly changing climate. His work spans wide array of market expertise, and includes a primary focus on office buildings, education, civic and culture, mixed-use, sports, and media projects. As a co-author of Gensler’s Impact by Design publication, Anthony has the unique ability to navigate the impact of opportunities at a very broad scale while simultaneously working through the details that individual projects need as they contribute to the greater mission.
Minor in Climate Change and Sustainability Policy
https://soe.lau.edu.lb/departments/civil/degree-programs/climasp.php
The development of this minor is a result of a funded project through a CONSORTIUM AGREEMENT ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF TEMPUS PROJECT “Development of an Interdisciplinary Minor Program on Climate Change and Sustainability Policy-CLIMASP” (Reference No. 543879-TEMPUS-1-2013-1-GRTEMPUS-JPCR) (Grant Agreement No. 2013-5043/001-001).
CLIMASP minor curriculum is designed to provide undergraduate students from different majors the flexibility to select courses to enhance their interests in climate change and to enrich their major field of study with professional skills in climate change adaptation policies and planning.
CLIMASP offers students a unique inter/multidisciplinary understanding of climate change. It provides a shift from a strict disciplinary orientation focused on natural sciences to other issues related to science, engineering, education, economics, sociology, architecture, etc. In fact, choosing a minor combined with a major enables student to pursue an area of interest with considerable employment possibilities by acquiring the necessary knowledge and skills.
Minor in Environmental Science
Minor in Environmental Science- Administered jointly by the Department of Civil Engineering and the Department of Natural Sciences
Overview
The Minor in Environmental Science is an interdisciplinary program administered jointly by the Department of Civil Engineering and the Department of Natural Sciences. The purpose of the program is to provide students with a broad conceptual framework for understanding environmental issues, from a global perspective.
Mission
The Minor in Environmental Science aims at providing a quality education to students interested in enriching their knowledge of existing global environmental issues and problems. It exposes them to important issues related to environmental problems and their causes. Concepts in environmental ethics, management and policies concerning the preservation of the environment are also provided. Additionally, the program covers topics related to the study of natural and non-natural chemical and microbiological substances in the environment and their transformations, and discusses methods of remediation to most environmental pollution issues.
Educational Objectives
The Minor in Environmental Science aims at providing students with:
- an understanding of the social, economic, political and legal framework of environmental issues,
- sufficient background to be able to collect, analyze and formulate possible solutions to environmental problems,
- an understanding of the intertwining effects and impacts of human activities on the world’s vital natural resources, and
- better job market opportunities.
Student Outcomes
- Understand the underlying concepts and principles associated with environmental science.
- Identify sources of water, soil and air pollutants.
- Demonstrate familiarity with the practical/field dimensions of a range of environmental problems and issues.
- Understand the interrelationships between society, economy and environment.
- Ability to critically review environmental impact assessment reports.
- Discuss remediation strategies of a variety of environmental contaminants.
- Recognize potential harmful role of human being in shaping the environment.
MS in Civil & Environmental Engineering
This comprehensive master’s degree program, offered by the Civil Engineering Department at LAU, imparts a sound professional and academic training in civil engineering. Students opt for one of five emphases:
- Construction Engineering and Management
- Environmental and Water Resources Engineering
- Geotechnical Engineering
- Structural Engineering
- Transportation Engineering
Wider career prospects
A research-oriented master’s degree program opens up the possibilities of a doctoral degree and an academic career. It also equips graduates with a deep understanding of the role of research in their industry. Through acquired research skills and a higher level of critical thinking, MS graduates are able to make more substantial contributions to the future of the profession.
Breadth and depth of knowledge
Through this program, students gain access to a variety of topics in their preferred area of study. They also get in-depth experience in one or more fields of civil engineering and are exposed to cross-disciplinary issues and topics related to the engineering and management of systems.
The research edge
Research is a major component of the curriculum. In addition to conducting research along with their studies, each student completes the program with a thesis based on a topic selected from their preferred emphasis area.
A dynamic faculty
Our civil engineering faculty brings excellent qualifications from renowned programs in the U.S. and Europe. Continuously engaged in cutting-edge research, our faculty has published over 250 refereed journal and conference articles, and received research grants from local and international funding agencies.
Best-in-class labs
Students have at their disposal some of the best-equipped labs in the country. Designed to support research as well as learning, the labs allow for measurement, testing, and experimentation under internationally accepted standards and procedures.
Available Scholarships
Scholarships and Assistantships.
All applicants are encouraged to contact faculty members with areas of research matching their interest.
To find out about the Graduate Assistantships application deadline, check with the Department’s main office.
Read on for further details about the program.
Mission
The mission of the graduate program in Civil and Environmental Engineering at LAU is to provide students with a well-rounded set of career skills that empowers them to address a wide range of problems through exposure to an advanced body of knowledge and scholarly endeavors.
Program Educational Objectives
The purpose of the Graduate Program in Civil and Environmental Engineering is to:
- Train students to develop the methodology and necessary skills to explore emerging issues in engineering and science.
- Provide students with an advanced background and a focused body of knowledge required for the present day professional practice in their chosen field of study, and to prepare them to adapt to a changing profession.
- Train the students in an active research environment, to equip them with the latest tools of research, and to prepare them for further study toward a Doctoral Degree.
Student Outcomes
Graduates of the MS - CEE programs will be able to:
- Reinforce skills developed in the undergraduate program.
- Use advanced analytical, computational, and/or experimental aspects of civil engineering.
- Make critical judgments based on a sound knowledge base.
- Conduct research and appreciate its importance in the evolution of civil engineering.
Environmental Lab
This lab has a full range of standard equipment for performing routine environmental analyses of unit processes and operations in water and wastewater treatment, water quality parameters, investigations in fresh and marine water quality, solid waste characterization and properties, evaluation of treatment processes, digestion and co-digestion, reactor performance, solid waste management, environmental impact monitoring, and environmental site investigations.
It is equipped with sampling devices and quality analysis of water/wastewater, jar tests, stream gauging, top of the line point and depth sediment samplers, bed load samplers, fluorometers, UV-visible spectrophotometers, colorimeters, peristaltic pumps, gas meters, centrifuges, incubators, and furnaces, in addition to mobile environmental monitoring stations for air pollution field measurements.
Energy Saving and Water Conservation

Energy Saving
Currently LAU consumes around 24 million kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electric energy and 5 million kWh of thermal energy per year, generating the equivalent of the CO2 emissions produced by around 7,000 cars.
Recognizing the importance both of environmental sustainability and of maximizing our community’s ability to work to its fullest capacity, we are constantly exploring ways to conserve energy, operate efficiently, and introduce renewable energy sources

Water Conservation
 |
Our campuses use around 100,000 m3 of water annually, enough to fill nearly 40 Olympic swimming pools.
We are tirelessly working to reduce our water consumption, harvest rain water and recycle gray water for irrigation. |
Here is what we are doing to achieve these goals:
Green Awareness
We are continuously sensitizing the LAU community about the importance of energy and water resources and their conservation and actively engaging them in this endeavor.
 |
We have launched an awareness campaign with tips for saving water on campus, in dorms, or at home. Posters were placed in restrooms and on bulletin boards throughout LAU, coupled with a short video on campus TV screens, the LAU website, and social media channels. |
 |
On August 26, 2022, the LAU Facilities Management Department in collaboration with the Association of Energy Engineers – Lebanon Chapter organized a site tour for LAU and non-LAU students. This initiative was part of the “internship in energy and sustainability” program by AEE Lebanon. Interns got the chance to tour the Byblos Campus, visit the High Performance Infrastructure Utilities as well as the LEED Gold Joseph Jabbra Library and Riyad Nassar Central Administration buildings. |
Measure It to Manage It
A metering plan is underway for the whole university to establish benchmarks and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for continuous resource monitoring and management.
Pilot projects are underway at the Gilbert and Rose-Marie Chagoury Health Sciences Center and the Tohme-Rizk Building in Byblos, as well as the Adnan Kassar School of Business and Wadad Sabbagh Khoury Student Center in Beirut.
Energy Efficiency and Renewables
We are implementing projects to reduce energy consumption and generate energy from renewables.
- The Byblos Library and Riyad Nassar Central Administration project features power and hot water generation from the sun.
- The same building will feature a solar tracking system.
- Beirut’s Wadad Sabbagh Khoury Student Center has been outfitted with a solar water heating system.
- Preliminary studies are underway for the introduction of solar water heating at Beirut’s indoor pool and the Byblos dorms.
- Several new and renovated classrooms and offices feature occupancy sensors that automatically regulate air-conditioning and lighting.
- CO sensors control the operation of the ventilators at the Byblos Underground Parking proportionally to the pollution level.
- We are currently retrofitting low consumption lighting fixtures throughout the university.
Water Efficiency and Re-use
We are implementing projects to reduce water consumption, harvest rain water and recycle water for irrigation.
- We have tested water saving devices in offices and dorms and implemented the same at the Tohme-Rizk building in Byblos as a pilot project, achieving savings of around 29 percent.
- Our Byblos campus features wastewater treatment plants. Treated water is being reused for irrigation, which will be further increased with the upcoming Byblos infrastructure project.
- The Byblos Library and Riyad Nassar Central Administration project features rain water harvesting and reuse.
- The Byblos Library and Riyad Nassar Central Administration project has been designed with low flow sanitary fixtures, achieving 35 percent water use reduction.
- We have surveyed all the water fixture types on the Byblos campus and are currently drafting a master plan to determine and implement possible further water saving measures.
Certify Your Space (initiative in progress)
We invite all departments, offices and units to implement sustainable practices into your day-to-day operations. This will motivate and engage participating staff to lower waste and consumption habits, improving their overall environmental performance while saving energy and water and reducing costs.
The Physical Plant will recognize your work by certification, installing a plaque at your office in recognition of your achievement. We will also list your office online on LAU’s list of certified green offices.
WATER CONSUMPTION & EXPENDITURE (updated November 2022)
| BEIRUT CAMPUS | BYBLOS CAMPUS | |
|---|---|---|
| Total Water Consumption (m3) | 26,000 | 65,000 |
|
Total Water Expenditure ($) *(excluding treatment & energy) |
57,600 | 10,194* |
| Water Use Index WUI (m3/student/y) | 5,96 | 17,89 |
| Water Cost Index WCI ($/student/y) | 13.2 | 2.81 |
| Water Cost Index WCI ($/m2/y) | 0.76 | 0.1 |
| Reclaimed Wastewater for Irrigation (m3) | N/A | 2,280 |
| Harvested Rainwater (m3) | 550 | 1,050 |


Sustainable Living
Tips for Green Living
We provide members of our community with practical, everyday green tips, helping them to lead a sustainable life style and join us in turning LAU into a green facility
The Green Pledge
The Green Pledge is an agreement to make small, simple choices in your daily life to help make our campus more sustainable. These small changes will add up to a big impact if we all do it together.
Join other students, faculty and staff who have already committed to sustainable behavior.
Take The Green Pledge
Your name will be featured among LAU’s committed green community.
The Green Calendar
Our green calendar identifies one anchor green day per semester and links it to activities that encourage the LAU community to go green.
- Earth Hour 2020
Raising the voice from home, LAU celebrates Earth Hour 2020, spreading a message of sustainability and connection to our planet within our community.
Check our community’s Earth Hour 2020 #LightsOffLAU Home Challenge on Instagram and Twitter for more photos and videos.
- Earth Hour 2019
On Saturday, 30 March 2019, LAU took part in the global “Lights Off” for one hour (8:30PM to 9:30PM), joining the world communities in solidarity with our Planet Earth #CONNECT2EARTH. We pre-celebrated Earth Hour on Thursday, March 28th, on both campuses, where hundreds of students, faculty and staff stepped-up in joining the global connect2earth.org movement. You can also check Earth Hour 2019’s Moments.
- Earth Hour 2018
On Saturday, 24 March 2018 at 8:30 p.m., the Lebanese American University joined millions of people across the globe in switching off the lights of our business premises and our homes for one hour as part of Earth Hour, the world’s largest grassroots movement for the environment. By taking part in this global “LIGHTS OUT” event, we continued acknowledging our commitment to #Connect2Earth this Earth Hour.
- Earth Hour 2017
We celebrated Earth Hour 2017 on Saturday March 25th, in what has become an LAU tradition. This year, we added a special touch to the event by gathering with the students to lighten candles and celebrate on both campuses. You can also check Earth Hour 2017’s Moments.
- Earth Hour 2016
In 2016, for the second year in a row, LAU joined the international movement and switched off its lights on Saturday, March 26th, for one hour in solidarity with global efforts to change climate change, our aim is to shine a light on vital climate action.
- Earth Hour 2015
“Earth Hour 2015” was held on March 28th with great success and the event’s video footage scored around 10,000 views on the LAU Facebook page.