SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
LAU actively contributes to SDG 16 by embodying principles of effective governance, justice, and accountable institutions across various facets of its operations. LAU’s governing bodies, including the Council of Deans, Student Affairs Council, Faculty Senate and Staff Advisory Council, play pivotal roles in advising on academic and student life matters, aligning with SDG 16’s focus on inclusive and transparent institutional governance. The Institute for Social Justice and Conflict Resolution (ISJCR) engages in dialogue on national policy issues, promoting justice and conflict resolution, while the Institute for Migration Studies (IMS) addresses displacement challenges, contributing to evidence-based migration policies. LAU’s Institute of Media Research and Training (IMRT) emphasizes transparency and trust in media, supporting SDG 16’s goal of accountable institutions. Additionally, LAU’s commitment to academic integrity and responsible research conduct further aligns with SDG 16, collectively reflecting the university’s dedication to fostering peace, justice, and strong institutions within its community and beyond.
Councils and Committees
Executive officers, faculty, staff, and student representatives, participate in university governance by serving on the following councils, committees, and other bodies. The mandates, compositions, terms, and methods of operation of these bodies are regulated by their respective bylaws.
President’s Cabinet
The President’s Cabinet acts as the top consulting and advisory body to the President on all matters that affect the well-being of the university. It ensures that the university is successfully meeting its mission, vision and goals. It has been operating since the summer of 2005.
Council of Deans
As the highest academic council, the Council of Deans leads all academic matters at the university, acting as:
An advisory body to the Provost and the President, and to other parties when it comes ot academic programs, processes, and procedures.
A liaison body among the heads of the academic units, promoting discussion and exchange of ideas on the effective management of their schools.
Student Affairs Council
As the highest student council, the Student Affairs Council acts as an advisory body to the Vice President for Student Development and Enrollment Management and the President, on all matters related to student life. It also serves as a liaison with all the relevant offices, regarding issues that affect student affairs on campus, to foster discussion and exchange of ideas on how to best serve students in a healthy and productive atmosphere.
University Planning Council
The University Planning Council serves as LAU’s collective think tank, bringing various entities together to discuss and develop methods and means that will assist the university in achieving its mission, vision and goals. It provides advice to the President on all matters relating to long- and mid-term planning, as well as strategic and conceptual university directives and goals.
Faculty Senate
The Faculty Senate, which includes some standing committees, is the main advisory body engaging faculty in LAU’s governance on issues such as academics, faculty status, operating budget, and more. It is composed of 34 members, equally allocated between the two campuses. In addition, each school elects departmental or divisional representatives to the Senate. For more information on the Senate functions, members, structure, constitution, bylaws, meetings, reports and relevant topics, visit the Faculty Senate website.
Standing University Councils of the Faculty
The standing university councils of the faculty provide policy and program leadership to all areas of the university. Faculty members of councils representing schools are elected by the school’s full-time faculty, while senate members of councils are chosen by the Faculty Senate. Student members of councils are elected by the students themselves. All elections of faculty members occur before the end of the spring semester, and new members assume their responsibilities at the beginning of the following academic year.
- Faculty Grievance Council
- Faculty Welfare and Promotion Council
- University Admission Council
- University Council for Financial Aid
- University Curriculum Council
- University Graduate and Research Council (UGRC)
- University Library and Information Resources Council
Staff Advisory Council
The Staff Advisory Council consists of elected representatives from each department to allow staff to participate in the governance of LAU. It serves as an advisory body and a forum for LAU staff members to voice their concerns.
Other Councils and Committees
- Campus Life Council
- Committees of Peers
- Institutional Review Board (IRB)
- Special Committees of the Faculty
The Student Councils
Every year, LAU students vote to elect 15 representatives to their “Campus Student Council.” Ten of the representatives also become members of the “University Student Council” that speak for all students when key decisions are made — for example matters related to financial aid, admissions, courses, campus activities, etc.
The representatives are available all year round to take suggestions from students.
Student Councils Representatives 2023–2024
University Student Council
|
Position |
Name |
School |
Campus |
|
President |
Engineering |
Byblos |
|
|
Vice President |
Adnan Kassar School of Business |
Beirut |
|
|
Secretary |
Pharmacy |
Byblos |
|
|
Treasurer |
Adnan Kassar School of Business |
Beirut |
|
|
Officer at Large |
Architecture & Design |
Beirut |
|
|
Representative – Curriculum |
Arts & Sciences |
Beirut |
|
|
Representative – Curriculum |
Arts & Sciences |
Byblos |
|
|
Representative – Financial Aid |
Arts & Sciences |
Beirut |
|
|
Representative – Financial Aid |
Adnan Kassar School of Business |
Byblos |
|
|
Representative – Integrity |
Graduate Programs |
Beirut |
|
|
Representative – Integrity |
Architecture & Design |
Byblos |
|
|
Representative – Library |
Arts & Sciences |
Beirut |
|
|
Representative – Library |
Arts & Sciences |
Byblos |
|
|
Representative – Admissions |
Adnan Kassar School of Business |
Beirut |
|
|
Representative – Admissions |
Adnan Kassar School of Business |
Byblos |
Academic School Council
|
School |
Name |
Campus |
|
Architecture & Design |
Beirut |
|
|
Arts & Sciences |
Beirut |
|
|
Adnan Kassar School of Business |
Beirut |
|
|
Engineering |
Byblos |
|
|
Graduate |
Byblos |
|
|
Alice Ramez Chagoury School of Nursing |
Byblos |
|
|
Pharmacy |
Byblos |
Beirut Campus Student Council
|
Position |
Name |
School |
|
President |
Adnan Kassar School of Business |
|
|
Vice President |
Arts & Sciences |
|
|
Secretary |
Arts & Sciences |
|
|
Treasurer |
Adnan Kassar School of Business |
|
|
Officer at Large |
Arts & Sciences |
Byblos Campus Student Council
|
Position |
Name |
School |
|
President |
Pharmacy |
|
|
Vice President |
Architecture & Design |
|
|
Secretary |
Alice Ramez Chagoury School of Nursing |
|
|
Treasurer |
Engineering |
|
|
Officer at Large |
Engineering |
Academic Integrity
At LAU, you are part of a large and diverse learning community that invites you to experience university life to the fullest: you are protected from all forms of discrimination, and you are welcome to think and express yourself freely.
With freedom comes responsibility, especially as LAU prepares you for the outside world. Below are some highlights from the LAU Student Code of Conduct to help you navigate this social contract.
Academic Violations: Table of Sanctions
LAU strongly encourages you to review the below listed violations regarding cheating as stipulated in Student Code of Conduct.
|
Code # |
Violation |
First Offense |
Second Offense |
|
Cheating |
|||
|
2.2.1 |
Using material or equipment (including mobile phones, electronic tablets, i-pads, calculators, and other devices) that is not authorized by the instructor in an examination, project, or graded assignment |
zero on the deliverable with a warning |
F on the course with a warning |
|
2.2.2 |
Cheating, copying, collaborating with or aiding another Student in a manner not permitted by the instructor on an examination, project, or other graded assignment* |
zero on the deliverable with a warning |
suspension |
|
2.2.3 |
Distributing or aiding in the distribution of previous exams without authorization of the instructor |
double warning – suspension |
suspension – expulsion |
|
2.2.4 |
Stealing, reproducing, or circulating an examination or other graded assignment before it has been administered |
suspension |
expulsion |
|
2.2.5 |
Being the Administrator of a communication platform, adding names to a group communication platform, adhering to a group communication platform engaging in any form of cheating, reproducing exams, providing examination answers before, during, or after the examination has been administered |
suspension |
dismissal |
|
2.2.6 |
Impersonating another Student or allowing another Student to impersonate one’s self during an examination, presentation, or other graded assignment |
suspension for both |
expulsion |
|
2.2.7 |
Impersonating an assistant, staff member, or faculty member for the purpose of (a) proctoring examinations without authorization or permission or (b) obtaining confidential information regarding coursework or examinations |
suspension – dismissal |
dismissal |
*2.2.2 Cheating, copying, collaborating with, or aiding another Student in a manner not permitted by the instructor on an examination, project, or other graded assignment. If a student, graduate or undergraduate, requires additional assistance on any assignment, beyond what LAU provides (including but not limited to: the instructor’s help during office hours, the tutoring sessions of the University’s Academic Success Center, and/or the help of the University’s Writing Center), the student must notify the class instructor and get his/her approval to do so. The student must specify the name of the help provider (be it a peer LAU student, a friend, a parent, a sibling, an alumna/us), external outsourcing, etc.), in addition to the nature and the scope of the assistance that will be provided.
Reach out if you need help!
Dedicated LAU counselors and academic advisors are available to help you with:
- Academic difficulties such as learning the language, test anxiety, or having second thoughts about your major.
- Building study habits, such as writing and note taking, time management, memory and concentration.
- Personal worries, such as health, relationship or financial stressors or balancing your time between work and studying.
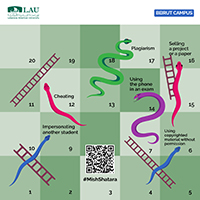
Awareness Campaign
Materials developed by LAU students under the supervision of the Student Life Offices.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Institute for Migration Studies
Overview
The Institute for Migration Studies (IMS) at the School of Arts and Sciences at LAU is an interdisciplinary, policy-driven and network-oriented research institute that develops research in the areas of Migration, Refugee and Displacement Studies. IMS serves as a resource center for graduate students, researchers, activists, policy analysts, humanitarian staff and scholars interested in the study of Migration and its various impacts on Lebanon and the MENA Region. In line with the overall mission of LAU, IMS aims to advance new narratives and intersectional approaches to the study of Migration through promoting research, generating studies, publishing the IMS’ working paper series and academic blog, organizing public webinars, conferences and workshops, as well as through its memberships in various regional and international networks.
Core Areas of Focus
Research
IMS provides multidisciplinary, independent and critical scholarship on factors determining and resulting from the migration and the forced displacement of populations. IMS drives scholarship and social scientific debates in the areas of Migration both through its own work and by fostering collaboration between graduate students, scholars and practitioners from a wide range of institutions and university departments. IMS additionally facilitates the research activities of local and international scholars and graduate students working on Migration and migrant communities in Lebanon and the MENA Region through connecting them to Key Informants, local actors and specialists working on the ground.
Teaching
The MA in Migration Studies at the Department of Social and Education Sciences at LAU is designed to support and develop the next generation of analysts, scholars and practitioners in the Migration, Refugee and Displacement spaces. IMS works closely with this program, and aims to foster a culture of critical reflection within the wider academic and humanitarian communities, and build upon theories of Migration to develop current and cutting-edge research that can serve as a foundation for later policy development. Along these lines, IMS hosts an annual Summer School, Internship Program, a Graduate Assistant Program, an Affiliate Program and a Visiting Fellowship Program (including at the Post-doctoral level).
Collaboration
IMS strives towards cooperation with international and local institutions, research centers and think tanks with similar agendas, as well as with Migration institutes in universities around the world. The objective is to establish an integrated institutional network for Migration research in Lebanon, the MENA region and beyond.
Dissemination
Through a variety of publications, webinars, workshops, conferences and networking initiatives, the IMS aims to foster engagement with a range of academics, policy analysts and practitioners.
LAU Navigates the Terrain of Climate-Induced Displacement
In collaboration with Rice University’s Baker Institute, the Institute for Migration Studies provided a medium for debate and proposed solutions to the challenges of migration in the MENA region.
Among the effects of climate change on the environment, it has become increasingly evident that the interplay between shifting climatic conditions and resource scarcity is shaping the patterns of migration.
In 2021, the World Bank’s Groundswell report revealed that climate change is one of the catalysts for migration and is projected to force more than 216 million individuals across six global regions to relocate within their national borders by the year 2050.
According to the report, the gradual onset of socially and environmentally damaging impacts left in the wake of climate change, among which are water scarcity, diminished crop productivity and rising sea levels, paint a daunting picture of displacement in the coming decades.
The urgency to address the intersection of climate, development, human rights and migration policy has never been more pressing given that a substantial proportion of individuals displaced by environmental changes are often compelled to cross international borders in search of safety and stability.
In an effort to address one of the gravest challenges of our time, the Institute for Migration Studies (IMS) at LAU partnered with Rice University’s Baker Institute to host a two-day workshop titled Climate-Induced Displacement in the Middle East and North Africa.
On October 9 and 10, the workshop dissected the multifaceted relationship between climate change and displacement, tackling topics on migratory patterns and the long-term effects climate-driven displacement has on the globe and its population.
The speakers also assessed host countries’ observance of the UNHCR’s 1951 Refugee Convention, an international treaty adopted in Geneva in July 1951 that sets out the legal definition of a refugee, enumerates their rights and privileges and outlines the legal duties and obligations of countries toward individuals who meet the refugee criteria.
IMS – an interdisciplinary, policy-oriented research institute – functions as a valuable resource hub for graduate students, researchers, policy analysts, humanitarian professionals and scholars with a vested interest in the study of migration and its implications in Lebanon and the MENA Region.
By inviting proposals for policy briefs and presenting them at the workshop, the institute aimed to encourage and facilitate collaboration among researchers and practitioners in the Middle East and North Africa who are actively engaged in the study and management of climate-induced displacement.
In panels featuring Professor in International Migration Law at the Faculty of Law at the University of Oslo Maja Janmyr, Deputy Director of Research at the Centre for Lebanese Studies Cathrine Brun and Title IX Director Jennifer Skulte-Ouaiss, the participants discussed how the MENA region is a hotspot for such a phenomenon given that it is characterized by an overlapping dynamic between climate change and conflict.
Not only is the MENA region extremely vulnerable to climate change, they noted, but also to social, economic and political factors that, together with climate change, could increase the probability of migration under duress, creating growing challenges for human development and planning.
“Today’s workshop is a chance to further that discussion and find points of intersection and divergences,” said IMS Director and Assistant Professor of Migration Studies Jasmin Lilian Diab. “We aim to produce a publication series that will expose to other researchers, policymakers and the general public the many ways that climate change will impact migration and refuge in the region.”
The first panel included discussions on the issues and constraints associated with the 1951 Refugee Convention when addressing this crisis, such as the absence of an inherent right for an asylum seeker to enter another nation, a lack of a precise definition of the term “persecution,” which is a fundamental component of the refugee definition and the absence of a more comprehensive alignment between the refugee definition and other human rights.
The panels that followed expounded on country-specific experiences and internal displacement as a human rights concern in the context of climate-induced predicaments, in addition to how proactive global action and far-sighted development planning could potentially reduce the number of climate migrants by tens of millions, thus addressing emerging climate change threats.
Given IMS’ core areas of focus between research, teaching, collaboration and knowledge dissemination, the panelists agreed that everyone has a role to play in the global dialogue about how to better manage and prepare for climate change and its effects. This should be done in the hopes of establishing a vital resource for policymakers, humanitarian organizations and other stakeholders advocating for evidence-based actions.
 |
The workshop dissected the multifaceted relationship between climate change and displacement, tackling topics on migratory patterns and the long-term effects climate-driven displacement has on the globe and its population. |
 |
In an effort to address one of the gravest challenges of our time, the Institute for Migration Studies (IMS) at LAU partnered with Rice University’s Baker Institute to host the two-day workshop on climate-induced displacement. |
LAU Releases Impactful Study on Media Uses and Trust During Lebanese Revolution
The report by the Institute of Media Research and Training surveyed the Lebanese at the height of popular protests about traditional and new media platforms.
Two-thirds (65.3 percent) of Lebanese said they supported the uprising but only about a quarter (27.9 percent) said they actually joined the protests, according to a research study released by the Institute of Media Research and Training (IMRT) at LAU.
The study – Media Uses and Trust During Protests – surveyed a nationally representative random sample of 1,000 Lebanese at the height of the ongoing protests (December 5-12).
According to the findings, released during a press conference at LAU, only 6.2 percent of Lebanese said they have had some media literacy training in their life, and almost half of surveyed Lebanese (46.2 percent) said they were currently unemployed.
The research was conducted by IMRT’s Media/War program and led by IMRT Director Jad Melki and IMRT Research Director Claudia Kozman. It was funded by LAU’s School of Arts and Sciences (SoAS) and the Office of Graduate Studies and Research (GSR).
“This study puts to rest all the rumors about how many people support and oppose the protests, which media stations have been followed or ignored and all the accusations against various Lebanese media,” said Dr. Melki at the press conference.
“It also helps news institutions and journalists to better understand new media habits and better serve their audiences.”
The study was also published in Arabic in Al-Adab Journal, making it accessible to a wider audience.
Al-Adab Editor Samah Idriss, who co-translated a summary of the report, said the significance of this study is “not limited to its findings, but also in the horizons that it opens for future studies.”
In the study, barely any Lebanese said they were members of political parties (3 percent) and that their allegiance to their sect was the most important (3.5 percent). In comparison, almost three-quarters said they were neither supporters nor members of any political party (71.4 percent) and that their allegiance to their country was the most important (72.6 percent).
The study explored which traditional and new media platforms – especially television channels and social media –the Lebanese people mainly accessed and trusted for news about the protests, and which media platforms they mainly engaged with to share news about the protests.
It found that the overwhelming majority of Lebanese followed television for news about the protests, with WhatsApp and Facebook coming in second and third place. Among the television channels, Al Jadeed, LBCI and MTV were the most followed and trusted.
The significance and timeliness of the study lay in the fact that such theoretical frameworks as media uses and selective exposure have rarely been applied to situations of unrest – a matter understudied despite the record number of protests and conflicts globally and the significant role of digital media in instigating, sustaining and propelling them.
“From a theoretical standpoint, this study confirms research about selective exposure, which underlines people’s tendency to expose themselves to media that align with their attitudes,” said Dr. Kozman. “Practically, the results indicate that Lebanese people read and watch media outlets that resonate with their beliefs about the protests.”
As an area plagued by continuous conflict and civil strife, the Arab region is ripe for research on conflict and media effects, which offers a better understanding of how news sources can deliver appropriate content to populations during dangerous and uncertain situations.
This study is part of a larger international project that examines media uses and selective exposure in other parts of the world affected by protests and unrest.
“We plan to release other working papers focused on national data in Iraq, Chile, Iran, France and Hong Kong and then some comparative studies about these countries,” said Dr. Melki. “The overarching goal is to apply theoretical questions and practical media-use questions to unusual situations.”
The press conference also launched a series of research seminars initiated by SoAS, with the aim of engaging the public and students in the research that the school’s various faculties are conducting, said SoAS Dean Cathia Jenainati.
In the same vein, Dr. Jenainati said “the power of the kind of research that IMRT is doing and the kind of research that Communication Arts at LAU is doing is that the end user, the reader, sees themselves in it.”
“The report reflects back to us what our behavior online means and the impact we have every time we send out that little tweet. It shows us that citizen activism is powerful, and we must engage in it.”
The study is part of the ongoing Media/War program, which covers a broad area of research that situates media research within the context of Arab wars, conflicts and politics.
Partnerships with government institutions:
LAU Signs MOU with the Ministry of Finance
https://news.lau.edu.lb/2018/lau-signs-mou-with-the-ministr.php
Drawing on its expertise and innovations, the university will help boost the ministry’s digital operations.
Under the patronage of the Minister of Finance Ali Hassan Al Khalil, LAU signed a memorandum of understanding on June 19 with the General Directorate of Land Register and Cadaster (GDLRC) headed by George Maarawi. The objective, as stated in the agreement, is “to execute joint educational, innovative and exchange programs related to elaborating cooperation in the fields of digital transformation and digital projects in general.”
Since adopting an automated system to facilitate the registration and retrieval processes at its Land Registry offices and Cadaster departments, the ministry has required the support of the private sector in implementing its projects. LAU will therefore offer its expertise and innovations, in the form of consultancies or task forces, within its mission to collaborate with the public sector in modernizing the state. The agreement will also provide opportunities for students through internships and hands-on experience.
During the signing, which took place at the ministry, Al Khalil described the event as a “milestone in the relationship between the public sector, represented by the Ministry of Finance, and the private sector, represented by the prestigious Lebanese American University, a leader in higher education in Lebanon that prepares our youth to keep up-to-date with progress worldwide.”
Commenting on the need to streamline the functions of the Lebanese administration in this digital age, Al Khalil referred to the ministry’s reliance on the expertise and spirit of LAU students in shaping the state’s future.
In response, LAU President Dr. Joseph G. Jabbra expressed his delight that the agreement falls within “the university’s mission to serve the community and the youth – our only hope for the advancement of Lebanon, not only locally but also internationally.” So long as there are leading figures, together with these young and women, he added, “Lebanon will prevail through its youth, and we will spare no effort or expense in educating and encouraging them.”
The importance of the MOU, says Senior Advisor to the President for Public Affairs Dr. Christian Oussi, is that it speaks to a common goal of both institutions – the country’s welfare. “While LAU strives to promote the youth and preserve the nation through education,” he said, “the Ministry of Finance works to achieve the security of the nation by ensuring economic stability and growth.”
The MOU follows hot on the heels of an agreement with the Lebanese Army – giving its members access to higher education at LAU – with the university’s longstanding support of the public sector dating back to collaborations with State Security and General Security.
“These agreements, activities and initiatives,” says Assistant to the President for Special Projects Saad El Zein, “reflect our concern toward the betterment of our social and community engagement, and strive for our country’s advancement by integrating our educational expertise with the public sector.”
SOE Takes On Traffic
https://news.lau.edu.lb/2019/soe-takes-on-traffic.php
Partnership with the Traffic Management Organization to pave the way for research and data analysis by LAU faculty and students.
From congestion to road design issues and a high number of vehicles relative to the population, the Lebanese traffic conundrum is no secret and has been the research focus of LAU’s own Associate Professor of Civil Engineering John Khoury.
In late June, LAU signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with the Traffic Management Organization (TMO) – a governmental division that operates under the Ministry of Interior – to establish a framework of collaboration, specifically with the Civil Engineering Department at the School of Engineering (SOE).
Dr. Khoury, who has also been a traffic advisor for TMO for two years now, initiated the collaboration, and will be leading a series of joint research projects related to the assessment of road traffic safety, the behavior of Lebanese motorists, road traffic rules and regulations, data analysis, and emergency management and traffic incident management in the case of accidents.
“These projects will produce recommendations for the TMO to implement, which will contribute to improving our traffic experience on Lebanese roads,” explained Dr. Khoury.
In fact, LAU’s own labs are well-equipped to serve this endeavor, in line with LAU’s strategic plan to become a university without borders, while bolstering its research output. Referring to the LAU Transportation Operations and Safety Center, Dr. Khoury declared that “we have a one-of-a-kind driver simulator that can help us create near real-life driving scenarios to assess driver reactions to specific triggers.” Apart from infrastructure, he added, the university has experts in the fields of transportation engineering, data analytics and human psychology who are able to make invaluable contributions to the research efforts.
Dr. Khoury will be working alongside Assistant Professor of Operations Management at the Adnan Kassar School of Business Jordan Srour, Associate Professor of Psychology at the School of Arts and Sciences Maria-Jose Sanchez-Ruiz, and a group of civil engineering graduates and undergraduates.
At the signing ceremony, LAU Provost George E. Nasr highlighted the students’ participation in addressing their country’s pressing problems. “While it’s the duty of the government to address our traffic problems, it’s also important for young people to be actively involved in devising the solutions for our country’s traffic problems.” As per the agreement, SOE senior students will also be able to enhance their career prospects by interning at the TMO for eight weeks.
TMO General Director Hoda Salloum noted that the collaboration with the university “empowers TMO with an academic, scientifically advanced edge.” She further hoped that this agreement will be the first of many steps to come in tackling traffic problems.
Partnership with the Ministry of Energy and Water Expands Prospects
https://news.lau.edu.lb/2019/partnership-with-the-ministry-of-energy-and-water-expands-prospects.php
Ministry seeks out SOE faculty and students and welcomes them to join forces for the future of energy in Lebanon.
The signing ceremony brought to the table Minister Nada Boustani, LAU President Joseph G. Jabbra, as well as university and ministry leadership.
LAU’s School of Engineering (SOE) is not new to taking initiative in serving Lebanon beyond campus gates. From traffic to e-mobility, artificial intelligence and pavement engineering, the school has time and again put its faculty, alumni and students at the forefront of developing solutions for the country’s most pressing needs.
To that extent, a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) was recently signed with the Ministry of Energy and Water (MEW) at the school’s seat on Byblos campus. The agreement will pave the way for closer interaction between the two institutions where SOE will offer academic consultancy to the ministry while the latter would allow for students to complete seminars and internship programs at the ministry.
The signing ceremony brought to the table Minister Nada Boustani, LAU President Joseph G. Jabbra, Interim Dean Raymond Ghajar – who was behind the initiative – as well as university and ministry leadership.
Dr. Jabbra welcomed the minister to LAU and thanked her for her faith in the young students’ potential. He reaffirmed the university’s strategic direction in expanding its academic and professional footprint beyond campus walls.
Following a tour of the SOE’s Engineering Laboratory and Research Center, Boustani hailed the initiative and commended the longstanding partnership between LAU – and particularly the SOE – and the ministry.
“Ten years ago, we started working together to prepare for the national plan for electricity, and our collaboration has never stopped since,” she declared, confirming that the partnership will remain steadfast as the ministry works on the improved plan which will be implemented under the supervision of the World Bank as well as other key donors.
Boustani expressed her hope in bringing SOE faculty and students’ “wisdom, expertise and independent thinking” to push the electricity plan forward.
Nutrition Students Put on Inspector’s Hat
MOU with Ministry of Industry will give students hands-on experience in food safety inspection.
https://news.lau.edu.lb/2019/nutrition-students-put-on-inspector-hat.php
Nutrition students will have the chance to conduct food safety inspections in factories across Lebanon thanks to an agreement signed on May 20 between the Ministry of Industry and eight universities, including LAU.
The Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) was signed by Minister of Industry Wael Abou Faour and Interim Dean of the School of Arts and Sciences Costantine Daher – representing LAU President Joseph G. Jabbra – at the Federation of Chambers of Commerce, Industry and Agriculture in Lebanon. Also present at the ceremony was Minister of Education Akram Chehayeb.
“Food safety and quality has become one of the essential subjects in universities,” said Abou Faour. “The MOU we are signing today will provide training for university students, who will take part in survey missions.” In return, the MOU will allow the ministry to carry out its campaign to ensure food safety and quality, he added.
Under the MOU, the ministry commits to welcoming undergraduate and graduate students interested in “food safety-related practical experience, vocational training, or in the framework of preparing for their theses.”
Students will assist ministry inspectors “in periodical inspections of food industries in order to ensure they adhere to the basic standards of food safety requirements.” The MOU also stipulates that students “write periodical reports following each field trip detailing their findings. The ministry team will use the report to draft a work plan that will help factories optimize their production quality.”
Interns will also assist in sample collection and will be in charge of their delivery labs for testing. At the end of their internship, they will receive certificates of participation signed by the minister and inspectors.
Daher was accompanied by Department of Natural Sciences Chair Sima Tokajian, Associate Chair Hussein Hassan and Coordinator of the Nutrition Program, Nadine Zeeni.
“Our collaboration with the Ministry of Industry started a few years ago when our department and LAU’s Continuing Education developed the first-of-its-kind advanced food safety certificate,” said Dr. Hassan, who is also associate professor of food science and technology, adding that a number of ministry inspectors have already received certificates as part of this collaboration.
Testament to the department’s impactful research in the field, the ministry has been using “our studies’ findings to develop policies and enforce measures to improve the wellbeing of Lebanese citizens,” he said.
The MOU is also an example of LAU’s active learning philosophy in accordance with its Third Strategic Plan.
“It goes hand in hand with our continuous efforts in the Natural Sciences department to increase our students’ exposure to learning activities that enhance their hands-on experience, so that they are better prepared to embark on their future career journey,” Dr. Hassan said.
Among such efforts are the department’s Food Science and Management Minor, and “a food production and safety rotation within the hospital internship that nutrition and dietetics interns undergo, in order to become licensed practitioners.”
In addition to LAU, the other signatories were the American University of Beirut, Saint Joseph University, Holy Spirit University of Kaslik, Beirut Arab University, the Lebanese University, University of Balamand and Notre Dame University.
The Lebanese Government’s Financial Recovery Plan Explained
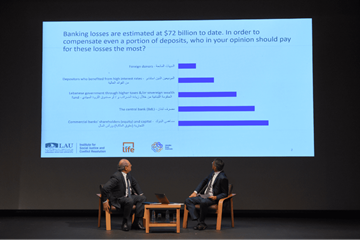
LAU hosts Deputy Prime Minister Saade Chami for a timely interactive discussion on the economic recovery program that aims to resolve, rather than manage, Lebanon’s financial crisis.
In an attempt to shed some light on Lebanon’s ongoing negotiations with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to tackle the country’s financial and socioeconomic meltdown, LAU’s Institute for Social Justice and Conflict Resolution (ISJCR), in partnership with LIFE Lebanon and the Middle East Institute (MEI), hosted an interactive fireside chat with the Lebanese Deputy Prime Minister Saade Chami who is leading the Lebanese negotiating team.
The two-hour event, held on July 13 on Beirut campus, was an opportunity for the general public to get some clarity on recent developments in the negotiations and voice their concerns. The discussion was driven by questions from online participants, interactive polls, and a Q&A that reflected public sentiment on core social, financial and economic issues.
In a candid and open conversation moderated by World Bank advisor Ronnie Hammad, Chami detailed the pending hurdles and the steps needed to resolve – rather than perpetually manage – Lebanon’s debilitating crisis.
“Every single person in this room, and following online, has been impacted one way or another by the ongoing economic meltdown,” noted Assistant Professor of Political Science and International Affairs and ISJCR Director Fadi Nicholas Nassar in his opening remarks. The discussion, he added, fell in line with the institute’s and LAU’s shared vision of “fostering a space that brings together decision makers, academics and the broader public, while encouraging meaningful—even if critical—dialogue on national policy issues.”
Since the recovery plan was never fully communicated to the public, the purpose of the event, stated Hammad, was to “have a collective understanding of the problem that we are facing, get some details about the recovery plan, and understand the implications of the plan on the vulnerable and what it may mean for us.”
Fielding questions as they were received online, Chami addressed issues that have mystified the Lebanese, from the sudden onset of the economic crisis – a crisis, which, he clarified, had actually been simmering since 2011 but was managed with financial engineering to buy time – to the measures needed for recovery, and whether there was any hope of redressing the situation with some compensation to depositors.
Ensuring macroeconomic stability, he explained in response to one question, was a prerequisite to economic stability, and should be implemented regardless of the negotiations with the IMF. This entails fighting corruption in governance, reducing poverty, unifying the Dollar-to-Lebanese Pound exchange rate, reaching fiscal sustainability to reduce debt, and conducting state-owned enterprise reforms, starting with the notorious power sector.
Here, he added, time was of the essence, as the country’s deficiency currently stood at $72 billion, having risen from an estimated $69 billion in October 2021.
On the suggestion of using state assets to pay off bank depositors, Chami clarified that “Lebanon’s assets, such as gold, should be off the table, as we cannot deprive the budget of these resources – which ultimately are shared with future generations – to compensate a few thousand depositors.” Even if we were to consider this option, the value of the state assets, as it currently stands, “would require 60 years to plug the gap in the financial system.”
Nor can we count on oil and gas revenues, he stated, as “at the moment, we do not have full clarity over the value of Lebanon’s oil and gas, and whether it even exists. It is out of the question.”
So, who should bear the brunt of the bank losses?
Chami called for “respecting the hierarchy of claims,” which starts with looking into the commercial banks’ capital. Based on the internationally acknowledged Bank Resolution Law, he said, existing shareholders and some of the depositors can take part in securing recapitalization for the banks. Ultimately, this will decide the fate of the banks – whether they will survive, merge with other banks or cease to exist.
Diplomats, bankers, business owners, risk strategists, academics and students in attendance probed Chami on the role of the government in managing the crisis, and raised a number of points such as accountability, regaining confidence in public institutions and the banks, and the likelihood of economic growth, among other topics.
Positive developments, such as moving in the direction of lifting banking secrecy, would pave the way to transparency and accountability, he explained. In this regard, a forensic audit of the Central Bank could set a precedent for auditing other governmental institutions.
To questions regarding the impact of capital controls on economic growth and the insufficiency of IMF funds to cover the shortfall, he explained that fresh money was not subject to capital controls and that the IMF deal is not meant to make up for the deficit but to inspire confidence in foreign investments.
“A deal with the IMF is key,” he contended, which is why it was developed with the collaboration of multiple stakeholders, including bankers, labor union representatives, financiers and economists.
“We are hoping that the political establishment understands the severity of the economic situation, and accepts the reforms in parliament,” added Chami, acknowledging the persistence of public mistrust in the government – “an expected result of years-long economic mismanagement and misguided policies.” That said, he was adamant that there was hope for a deal with the IMF, citing “no major objection by any of the political parties.”
“The country can be put on the right path in a matter of a few months,” he reiterated, confident that once the needed reforms are met, “we can begin to get us out of the crisis within five years.”
 |
The discussion was driven by questions from online participants, interactive polls, and a Q&A that reflected public sentiment on core social, financial and economic issues. |
 |
In a candid and open conversation moderated by Hammad, Chami detailed the pending hurdles and the steps needed to resolve – rather than perpetually manage – Lebanon’s debilitating crisis. |
 |
The discussion, as Dr. Nassar pointed out, fell in line with the institute’s and LAU’s shared vision of “fostering a space that brings together decision makers, academics and the broader public, while encouraging meaningful—even if critical—dialogue on national policy issues.” |
RESPONSIBLE CONDUCT OF RESEARCH AND RESPONDING TO ALLEGATIONS
1.PURPOSE
The Lebanese American University (LAU) recognizes its commitment to its researchers and the community it serves to ensure the highest ethical standards based on integrity and professionalism in the conduct of research. By fulfilling its mission, the LAU encourages its researchers and faculty to partake in research and professional activities while protecting the concerned community from any form of research misconduct and false allegations.
This Policy provides the guiding ethical and legal principles for the responsible conduct of research and this applies to all those undertaking research at the University and its affiliated facilities (healthcare or otherwise) or on its behalf.
LAU follows this Policy, and relevant procedures, for
- The resolution of allegations of research misconduct,
- Determining threat or harm to the concerned community, sponsored funding and/or integrity of research, and
- Determining the appropriate course of action.
This Policy is intended to carry out LAU’s responsibilities in compliance with, but not limited to, the LAU’s Code of Ethics, LAU’s policies and procedures pertaining to research, and relevant national and international regulations pertaining to the responsible conduct of research, including those applicable to sponsored awards received by LAU.
2. DEFINITIONS
2.1.Deciding Official (DO) means the institutional official who makes final determinations on allegations of research misconduct and any institutional administrative actions. The Deciding Official will not be the same individual as the Research Integrity Officer and should have no direct prior involvement in the institution’s inquiry, investigation, or allegation assessment. A DO’s appointment of an individual to assess allegations of research misconduct, or to serve on an inquiry or investigation committee, is not considered to be direct prior involvement. For the purpose of this Policy, the DO is the LAU President.
2.2. Fabrication is making up data or results and recording or reporting them.
2.3.Falsification is manipulating research findings, materials, equipment, or processes, or changing or omitting data or results such that the research is not accurately represented in the research record.
2.4.Plagiarism is the use of another person’s ideas, processes, results, or words without giving appropriate credit or acknowledging the author, or obtaining their consent.
2.5.Research is defined as a systemic investigation, including research development, testing and evaluation, designed to develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge.
2.6.Research Integrity Officer (RIO) means the institutional official responsible for: (1) assessing allegations of research misconduct to determine if they fall within the definition of research misconduct, and warrant an inquiry on the basis that the allegation is sufficiently credible and specific so that potential evidence of research misconduct may be identified; (2) overseeing inquires and investigations; and (3) the other responsibilities described in this document. For the purpose of this document, the RIO is the Provost.
2.7.Research Misconduct is defined as fabrication, falsification, or plagiarism in proposing, performing, or reviewing research, or in reporting research results.
2.8. Responsible Conduct of Research is defined as “the practice of scientific investigation with integrity.”
3. RESPONSIBILITY
3.1. All Faculty, Staff, Students of the University and its affiliated health care facilities, as well as visitor researchers (if applicable) should adhere to the principles highlighted in this document and report any form of research misconduct as stated in the LAU Procedures for Responsible Conduct of Research and Responding to Allegations.
3.2. The Office of Graduate Studies and Research is responsible for informing, providing awareness and educational seminars, online training and support to faculty, staff and students to ensure responsible conduct of research.
3.3. The Office of Graduate Studies and Research is responsible for implementing, updating this Policy and relevant procedures and ensuring compliance with its terms.
3.4. The DO will make a final determination of the alleged research misconduct following the procedures set forth in the LAU Procedures for Responsible Conduct of Research and Responding to Allegations.
3.5. The RIO, in coordination with the Office of Graduate Studies and Research, the General Counsel’s Office and in line with sponsored award requirements, shall coordinate any required reporting or submissions to the concerned awarding agencies.
4.SCOPE AND APPLICABILITY
4.1.This Policy applies to all researchers conducting research under its auspices including faculty, staff and students as well as visitor researchers (if applicable).
For the purpose of this document, a finding of research misconduct requires that:
4.1.1. There is a significant departure from accepted practices of the relevant research community
4.1.2. The misconduct is committed intentionally, knowingly, or recklessly,
4.1.3. The allegations to be proven by a preponderance of the evidence
For the purpose of this document, research misconduct does not include differences of opinion.
Furthermore, this Policy does not apply to authorship or collaboration disputes and applies only to allegations of research misconduct that occurred within six years of the date the institution or sponsored awards agency received the allegation.
4.2. This document applies to allegations of research misconduct as defined above for the fabrication, falsification, or plagiarism in proposing, performing, or reviewing research, or in reporting research results involving:
4.2.1. Any person, including a faculty member, staff member and/or student who, at the time of the alleged research misconduct, was employed by, as faculty or staff, or was affiliated by contract or agreement with the institution (research collaborators must be made aware of this document) as well as graduate or undergraduate student working under the supervision of a faculty or staff. This also includes members of the faculty research councils /committees within the schools, University Research Council, Institutional Review Board, or any other related Advisory Board or committee).
4.2.2. Any form of research proposed, performed, reviewed or reported, regardless of whether an application or proposal for funds resulted in a grant, contact, cooperative agreement, or other form of funding support related to Sponsored Awards.
This document does not apply to authorship or collaboration disputes or non-compliance related matters pertaining to human or animal research. Concerns regarding non-compliance and violations pertaining to ethical conduct of research involving humans / animals must be reported to the LAU Institutional Review Board for Human participant research.
5. STATEMENT OF POLICY
5.1. LAU will encourage a strong research culture that will demonstrate strong commitment to responsible conduct as per below principles, by actively promoting awareness/training and maintaining an environment of ethical behavior of research.
5.1.1. Integrity
- Oversee and comply with all relevant regulatory and ethical requirements for the conduct of research within LAU and any collaborative organization/institution
- Ensure securing necessary approvals, as it is required, to conduct the research
- Demonstrate accountability of awarded research funds and comply with the specific terms and conditions related to research contracts and grants
- Foster and support honesty in research, in relation to your own research and that of others
5.1.2. Ethical Conduct
- Comply with all relevant regulations, local and international laws or legislations as well as the University’s Policies and Procedures for the conduct of research and the protection of human participants, when applicable
- Secure Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval for all research involving human participants or participants’ information
- Ensure the highest standards of honesty, integrity, accuracy and objectivity
5.1.3. Individual responsibility, Training and Skills
- Conduct the research in accordance with this code and all applicable laws, policies and procedures
- Exercise sound judgement and serve in the best interests of the institution and the community
- Identify and undertake the necessary training and development to carry out the proposed research.
5.1.4. Conflict of Interest
- Recognize and disclose any potential or perceived professional or non-financial conflict of interest relating to any aspect of the research conducted
- Recognize and disclose any form of actual or perceived financial conflict of interest, and or receipt of any form of financial or benefit from a third party relating to any aspect of the research conducted
5.1.5. Compliance
- Ensure that any research undertaken complies with an approved research project, agreements, terms and conditions relating to the project while maintaining proper governance and transparency
- Comply with multi-institutional agreements when researchers are involved in joint research projects, particularly those relating to dissemination of research findings and management of the research data and materials
- Ensure the accuracy, security and accessibility of all research data
- Avoid plagiarism and use of other researchers’ intellectual property, ideas, or data without their proper consent
- Ensure that the data and results are retained or deleted/destroyed in accordance with all legal, ethical, funding organization and University’s requirements.
- Comply with all conditions specified by awarding agencies with respect to the research
5.1.6. Publication and Dissemination of Research Findings
- Disseminate a complete description and related findings of the research project as broadly as possible, including negative findings, results contrary to the hypothesis, and any changes or corrective actions
- Take into account any restrictions to intellectual property or culturally sensitive data
- Cite and acknowledge other relevant work appropriately and accurately when disseminating research findings
- Include information on all funding resources for the specific research and any potential conflict of interest
5.2. LAU will commit to a timely review of up to 90 days and resolution of allegations related to research misconduct that leads, as appropriate, to an inquiry or an investigation, as per the LAU Procedures for Responsible Conduct of Research and Responding to Allegations.
6. EFFECTIVE DATE
The foregoing Responsible Conduct of Research and Responding to Allegations Policy was adopted by the Board of Trustees on March 21 & 22, 2019 and is effective as of March 22, 2019.
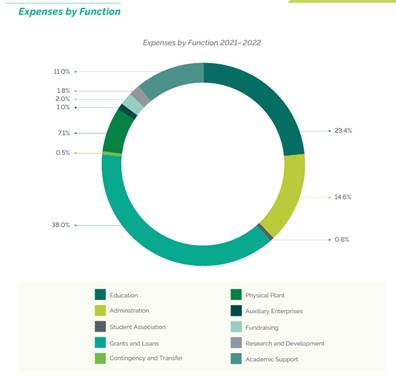
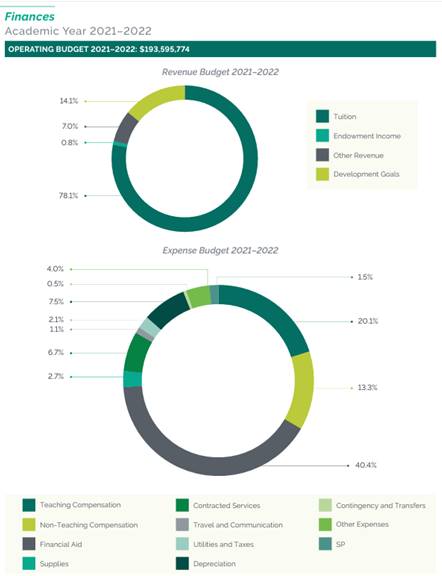
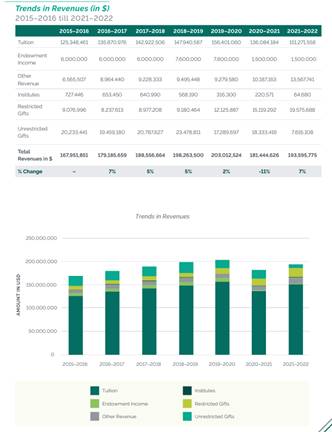
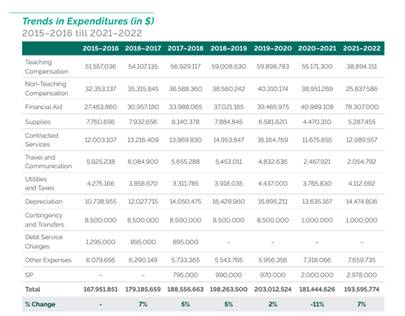
Fact Book – Financial Information